Raped, tortured, imprisoned: the Iranian women fighting for their daughters’ future
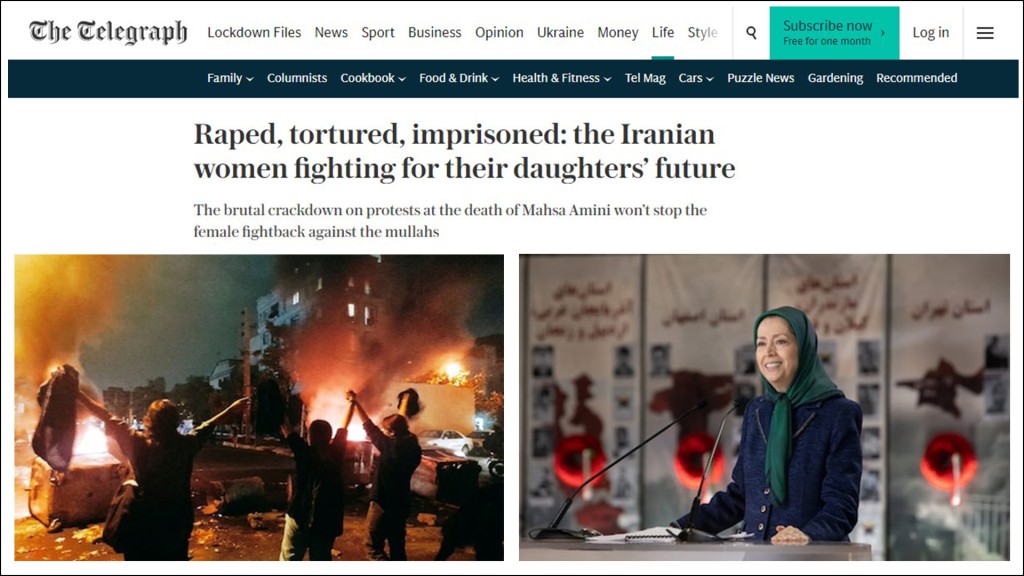
The brutal crackdown on protests at the death of Mahsa Amini won’t stop the female fightback against the mullahs
Lying in a coma with bandages around her head and breathing tubes protruding from her nose and mouth – this was the social media image that saw the brutality of the Iranian regime go viral.
For decades, the barbarism of supreme ruler Ayatollah Ali Khamenei’s misogynistic mullahs went largely unnoticed as thousands of Iranian women endured immense suffering and torture.
But when Jina “Mahsa” Amini, a 22-year-old Kurd, died after a “violent arrest” for infringing the country’s strict hijab rules, the Western world finally sat up and took notice.
Coming weeks after Ebrahim Raisi, Iran’s hardline president, ordered a crackdown on women’s rights, including stricter enforcement of the mandatory dress code, which has required all women to wear the hijab since the 1979 Islamic revolution, Amini’s senseless beating in the back of a police van sparked a wave of protests. (The police suggested the young woman had suffered a heart attack but her family disputed this, pointing out that she had not been experiencing any health problems.)
As many as 30,000 Iranian women have been killed in Iran over the past 40 years, but it was Amini’s death on September 16 last year that proved the final straw for the country’s brave female freedom fighters, who tore off their hijabs, cut their hair and adopted a rallying cry of “women, life, freedom”.
Iranian women remove their hijabs during a protest for Mahsa Amini CREDIT: PA
Female students have taken the lead, with demonstrations at 204 universities. Of the 1,776 schools where pupils joined protests, 1,186 were girls’ schools, underscoring the pivotal role of women in shaping the future of Iran.
What began as an outcry has snowballed into a revolutionary movement in a country that has long treated women as less than second-class citizens.
Forced to wear the hijab, even in primary school, unable to leave the country without their husband’s permission, blocked from studying certain subjects and forbidden from watching men’s sports in stadiums, women in Iran have been subjugated for generations.
Yet as the world marks International Women’s Day (IWD) today, Iran’s swelling feminist movement is showing no sign of slowing down – fuelled by a new era of Generation-Z rebels like Amini who refuse to be enslaved by their male rulers.
As Maryam Rajavi, the Iranian opposition leader and president-elect of the National Council of Resistance of Iran (NCRI), said in an IWD speech last weekend: “The uprising and unparalleled courage of Iranian women have captivated the attention of the world. Defiant girls from Tehran to Zahedan are shouting: ‘With or without the hijab, onward to the revolution!’
“For 30 years, we have been saying that the rise of women will ignite the uprising. The day will come when the women of Iran will overthrow the religious tyranny of the mullahs.”
The 69-year-old is co-leader of the People’s Mujahedin of Iran (MEK) dissident group, along with her husband Massoud Rajavi. She began her political activism at the age of 22 after her sister Narges, was killed by SAVAK, the Iranian state police, under the Shah’s rule. Her other sister, Massumeh, was executed while pregnant in 1982 under Ayatollah Khomeini’s regime. The MEK is calling for the peaceful transfer of power to the Iranian people following the overthrow of Khamenei, who succeeded Khomeini in 1989.
In 2006, Rajavi gave a landmark speech at the Council of Europe in Strasbourg when she called for “complete gender equality” in Iran including the right for Iranian women to “freely choose their clothing”.
“Any form of discrimination against women will be abolished,” she declared, spelling out her dream for a future Iran free of tyranny, with a modern justice system based on the rule of law and free democratic elections with women given equal participation in political leadership.
Back then, any hope of a pluralist, capitalist system – with church and state separated and censorship and inquisition banned – seemed like the stuff of fantasy as activists continued to be slayed and imprisoned for opposing the ruthless and repressive status quo.
But, 17 years on, the tide appears to be turning as growing numbers of women risk rape, torture, imprisonment and even death to give their daughters the freedom they have long been denied.
It has come at an extraordinary cost, with the MEK estimating that at least 750 protesters have been killed in the latest uprising – including 84 women and at least 70 children aged from two to 17. Most have been killed by gunshots but some have been fatally beaten with batons. The regime denies any role in the deaths.
In December, the judiciary carried out its first execution of a protester. A second was hanged from a crane in public. At least 30,000 activists are thought to have been arrested, subjected to physical and psychological torture, including sexual abuse, in particular against women.
With the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps manning most hospitals and the regime even monitoring the purchase of first-aid supplies, those injured during protests are forced to seek medical help under cover of darkness, tended to by a secret army of night doctors operating in covert resistance units.
This week, it emerged that more than 1,000 Iranian students – mostly schoolgirls – have fallen ill over the past three months in a reported wave of poisonings, possibly with toxic gas.
Dozens of girls in at least 26 schools reportedly fell ill last Wednesday, all reporting similar symptoms of breathing problems, nausea, dizziness and fatigue.
Yet the resistance movement continues to gather momentum as protesters, particularly those in their late teens and early 20s, use online virtual private networks to circumvent the country’s strict internet restrictions to co-ordinate the rebellion and get their voices heard.
According to Shahin Gobadi, a spokesman for the NCRI: “The resistance is continuing despite the crackdown. Iran is the country of revolutions but what we are currently witnessing is something very different from the Arab Spring.
“Young people have become much more organised and women, particularly, have been playing a pivotal role. In the past five months, 1,000 enemy compounds and 750 vehicles have been destroyed, using Molotov cocktails, largely thrown by women.
“This younger generation is much more outward looking. A lot of Iranians have satellite dishes and they can see that the world has changed. Protests have always been attended by people from all walks of life and all generations, but when you see Gen Zs –teenagers – becoming political, then you know the regime is in deep trouble.
“What we are witnessing, basically, is the culmination of 100 years of striving for democracy and human rights.”
Around 80 per cent of the population of Iran lives below the poverty line, despite the country having the third largest oil and second biggest natural gas reserves in the world in 2021. Yet despite four decades of poverty, unemployment, inflation, high prices and corruption, Gobadi says the protests are not about money. “It’s about freedom,” he says. “In previous times, when the regime attacked young people, [the young people] succumbed. But this time around, the mood is defiant. The duration of the protest – going on several months – it changes the psyche; it shows the regime isn’t invincible, that they can be forced back.”
Referencing Amini, he adds: “Sometimes a revolution is sparked by an incident that no one can predict. This killing of Mahsa, a 22-year-old woman, over a headscarf, has acted as a catalyst. It’s one thing for people to be disenchanted, it’s another to give them direction.
“Women have always been involved in the resistance movement but not on this scale. They feel they have much more to fight for. They are saying, look, we have no future for ourselves but this shouldn’t happen to the next generation. This can’t continue to happen to our daughters.”
- Tags: Human Rights, Iran's women, Women

